
Rate at which the network sends data in the environment (in MB/s). Rate at which the network receives data in the environment (in MB/s). Number of I/O written operations performed on the disk per second in the environment. Number of I/O read operations performed on the disk per second in the environment. Rate at which data is written to the disk in the environment (in MB/s). Rate at which data is read from the disk in the environment (in MB/s). Number of Load Balancers present in the environment.Īmount of CPU utilized by the AutoScaling Group (in percentage). Number of Templates present in the environment. Number of Launch Configurations present in the environment. Number of SQS Queues present in the environment. Number of AutoScaling Groups present in the environment. Number of EC2 instances present in the environment. Number of instances with 'No Data' health status. Number of instances with 'Warning' health status. Number of instances with 'Pending' health status. Number of instances with 'Info' health status. Number of instances with 'Unknown' health status. Number of instances with 'Severe' health status. Number of instances with 'Degraded' health status. Number of instances with 'OK' health status. ( Ok, Info, Unknown, No data, Warning, Degraded, Severe, Pending, or Suspended)

Shows the health status of the environment. ( Aborting, Launching, Updating, LinkingFrom,LinkingTo, Ready, Terminating, or Terminated) List view tab enables you to perform bulk admin configurations.īy clicking a monitor from the list, you will be taken to the AWS Elastic Beanstalk dashboard.Performance tab gives the health status and events for the past 24 hours or 30 days.Availability tab gives the availability history for the past 24 hours or 30 days.Displayed is the Amazon Elastic Beanstalk bulk configuration view distributed into three tabs: Click on the Elastic Beanstalk instance available under Amazon in the Cloud Apps section. Go to the Monitors Category View by clicking the Monitors tab. With Elastic Beanstalk, you can deploy and manage applications in the AWS cloud without having to learn about the infrastructure that is needed for those applications. For more information, see the following section "My instance is in stuck in the Pending:Wait or Terminating:Wait state during scaling activity".AWS Elastic Beanstalk is an orchestration service from Amazon which is used for deploying and scaling applications that orchestrates various AWS services like EC2, S3, Simple Notification Service (SNS), CloudWatch, AutoScaling, and Elastic Load Balancers (ELB). If there is a lifecycle hook, you might need to either complete the lifecycle hook or wait for the timeout period to end.
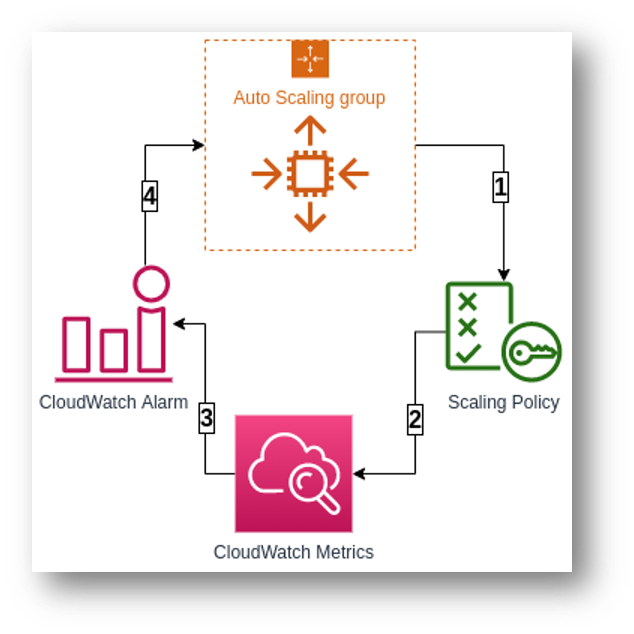
Check if there is a lifecycle hook configured for your Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group.For more information, see How do I ensure that Amazon CloudWatch alarms trigger scaling of my Auto Scaling group? Check your CloudWatch alarm to be sure that it's triggering scaling activity correctly.If you specified a warm-up time, the Auto Scaling group doesn't count instances toward the group metrics until after the warmup. If you're using a step scaling policy or target tracking policy, check for an in progress instance warmup.Simple scaling policies remain suspended until after the cooldown period. If you're using a simple scaling policy, check if your instances are in a cooldown period.Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling can't evaluate a health check replacement for suspended ReplaceUnhealthy or HealthCheck processes.

Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling can't evaluate a CloudWatch scaling policy for suspended Terminate, Launch, or Alarm Notification processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
